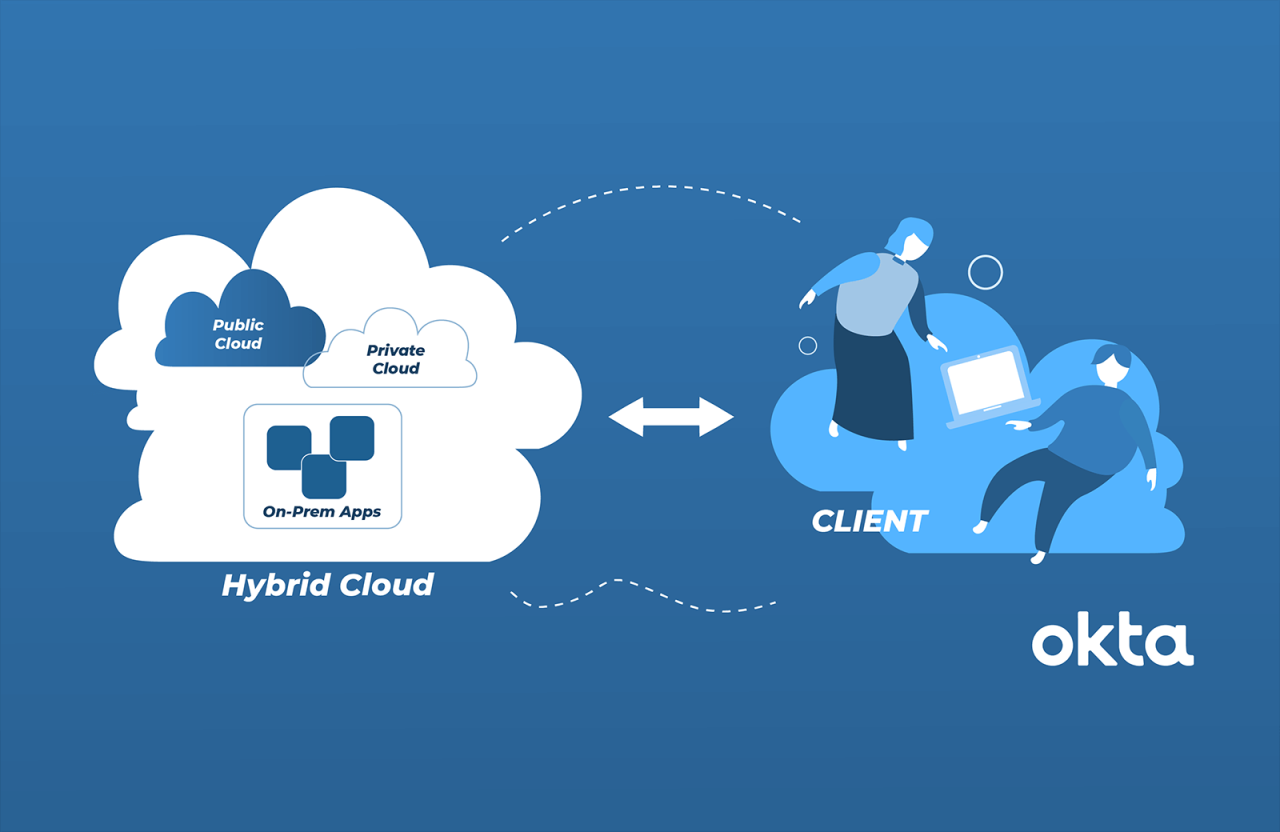
What are the benefits of a hybrid cloud architecture? This exploration delves into the advantages of combining private and public cloud environments, revealing a powerful solution for modern businesses seeking enhanced scalability, cost optimization, and robust security measures.
Hybrid cloud architectures offer a compelling blend of the best aspects of private and public cloud models. This approach allows businesses to leverage the scalability and cost-effectiveness of the public cloud while maintaining control over sensitive data and critical applications within their private cloud. The ability to tailor a solution to specific business needs is a key advantage.
Defining Hybrid Cloud Architecture
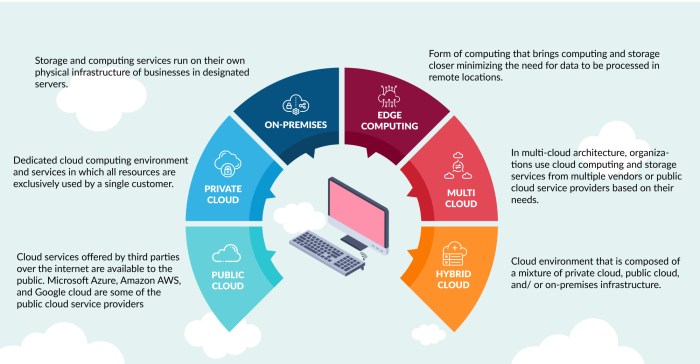
A hybrid cloud architecture strategically combines resources from both private and public cloud environments. This approach allows organizations to leverage the advantages of each model while mitigating potential risks. It offers a flexible and scalable solution, providing greater control over sensitive data and applications while benefiting from the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public cloud services.Hybrid cloud architecture is a powerful solution for businesses looking to optimize their IT infrastructure and enhance operational efficiency.
It enables organizations to manage diverse workloads and data sets effectively, adapting to fluctuating demands without compromising security or control.
Key Components of a Hybrid Cloud Setup
The successful implementation of a hybrid cloud relies on several key components. These components work together to provide a seamless integration between private and public cloud environments. Crucial elements include:
- Virtualization technology: This technology plays a pivotal role in enabling the abstraction of physical resources, enabling the seamless migration of workloads between environments. This allows for flexible resource allocation and utilization, as well as simplified management across diverse platforms.
- Networking infrastructure: A robust and secure network infrastructure is essential for connecting the private and public cloud environments. This ensures seamless data exchange and application access, minimizing latency and improving overall performance.
- Security tools: Robust security tools are crucial to safeguard data and applications in a hybrid cloud environment. These tools must be comprehensive enough to address the specific security needs of the organization, especially when dealing with sensitive data and regulatory compliance requirements.
- Management tools: Effective management tools are vital for orchestrating and controlling the hybrid cloud environment. These tools are instrumental in managing the diverse workloads, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization.
Types of Hybrid Cloud Deployments
Organizations can implement hybrid cloud deployments in various ways, each tailored to specific needs and requirements.
- Private cloud to public cloud: This model is commonly employed for disaster recovery, enabling the automatic transfer of critical workloads to the public cloud during emergencies. This strategy ensures business continuity, safeguarding against potential disruptions.
- Public cloud to private cloud: In this scenario, applications or data might be hosted on a public cloud but periodically migrated or backed up to a private cloud for enhanced security or compliance reasons. This approach ensures data security and compliance with specific regulations.
- Private cloud with public cloud extensions: Organizations may choose to extend their private cloud infrastructure with public cloud resources for enhanced scalability and cost-effectiveness. This allows organizations to seamlessly scale up their IT resources based on fluctuating demands.
Benefits of Using a Hybrid Cloud Environment
A hybrid cloud environment offers a multitude of benefits, contributing to improved operational efficiency and reduced costs.
- Enhanced scalability and flexibility: Organizations can easily scale their IT resources up or down depending on their needs. This adaptability is especially beneficial during periods of high demand or rapid growth.
- Improved cost efficiency: Organizations can optimize their cloud spending by using the public cloud for less critical workloads and reserving the private cloud for sensitive data and applications. This allows for a cost-effective and optimized cloud strategy.
- Enhanced security and compliance: Hybrid clouds provide greater control over sensitive data and applications, enabling organizations to comply with industry regulations and security standards.
- Improved disaster recovery: The ability to seamlessly move workloads to the public cloud during emergencies ensures business continuity and reduces downtime.
Comparison of Cloud Models
The following table summarizes the key differences between private, public, and hybrid cloud models.
| Feature | Private Cloud | Public Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ownership and Management | Owned and managed by a single organization | Owned and managed by a third-party provider | Combines private and public cloud environments |
| Scalability | Scalable but may require significant investment in infrastructure | Highly scalable and elastic | Scalable and flexible, leveraging the strengths of both models |
| Security | High degree of control over security | Security is the responsibility of the provider | Offers a balance of control and security |
| Cost | Potentially higher upfront costs but lower ongoing costs | Cost-effective for on-demand resources | Optimized cost structure, balancing private and public cloud usage |
Scalability and Flexibility
Hybrid cloud architecture offers a powerful combination of scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to optimize their IT resources based on specific needs and workloads. This dynamic approach leverages the strengths of both public and private clouds, enabling businesses to achieve a higher degree of control and efficiency compared to a purely public cloud model. The adaptability of hybrid cloud facilitates seamless transitions between environments, maximizing resource utilization and minimizing operational costs.Hybrid cloud architectures are particularly beneficial in scenarios demanding a balance between cost-effectiveness and control.
Organizations can deploy computationally intensive or sensitive data-processing tasks on their private cloud while utilizing the public cloud for less critical workloads or bursts of demand. This nuanced approach enables them to leverage the scalability of the public cloud without compromising the security and control inherent in a private cloud environment.
Hybrid Cloud Scalability
Hybrid cloud architecture significantly enhances scalability compared to a purely public cloud model. The ability to leverage both public and private cloud resources allows for dynamic allocation of resources, enabling organizations to adjust their capacity based on fluctuating demands. This elasticity is a key differentiator in a hybrid cloud environment.
Adapting Resources in a Hybrid Environment
Adapting resources in a hybrid cloud environment is highly flexible. Organizations can easily shift workloads between the public and private cloud components based on factors such as cost, performance requirements, and security needs. This dynamic allocation of resources allows for optimal resource utilization, minimizing costs and maximizing performance.
Comparison to Public Cloud
A purely public cloud model, while highly scalable in terms of raw capacity, often lacks the level of control and security that a private cloud offers. Hybrid cloud bridges this gap, providing a blended approach that combines the benefits of both models. The control over data and infrastructure in a private cloud allows for tailored security measures and compliance requirements that might not be readily available in a purely public cloud environment.
This nuanced approach allows for a more controlled and efficient deployment and management of resources.
Scenarios Benefiting from Hybrid Cloud Scalability
Hybrid cloud architectures excel in diverse scenarios requiring adaptability and control. For instance, a financial institution processing high volumes of transactions during peak seasons could leverage the public cloud for temporary increases in capacity, while maintaining sensitive data and core operations within the secure private cloud. Similarly, a company experiencing sudden spikes in demand for its online services can quickly scale up their public cloud resources without compromising the security and control of critical data and systems residing in the private cloud.
Scaling Resources Up and Down
Scaling resources up and down in a hybrid cloud environment is a streamlined process. Organizations can automatically provision resources on the public cloud to meet temporary increases in demand. This process often involves utilizing cloud management tools that can automate scaling based on pre-defined parameters or real-time metrics. Conversely, when demand subsides, resources can be de-provisioned or scaled down on the public cloud, optimizing costs and preventing unnecessary expenditure.
The use of automation tools significantly simplifies this process, reducing manual intervention and ensuring efficiency.
Data Security and Compliance
Hybrid cloud architectures offer a unique approach to data security and compliance, leveraging the strengths of both public and private clouds. This approach allows organizations to tailor security measures to specific data sensitivities and regulatory requirements, while maintaining flexibility and scalability. This approach is especially crucial in today’s increasingly complex regulatory landscape.A hybrid cloud’s ability to segregate sensitive data in a secure private cloud environment while leveraging the cost-effectiveness and scalability of a public cloud for less sensitive data, results in a robust security posture.
This careful segregation significantly enhances the organization’s ability to meet compliance mandates and mitigate risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access.
Security Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Architecture
Hybrid cloud architectures provide a multifaceted approach to data security. By combining the strengths of public and private clouds, organizations can implement a layered security model that protects sensitive data while maximizing operational efficiency. This approach allows for granular control over data access and encryption, resulting in a more secure environment compared to a single-cloud deployment. The segregation of sensitive data into a private cloud environment offers a higher level of control and security.
Addressing Compliance Concerns with Hybrid Clouds
Hybrid cloud architecture plays a critical role in meeting diverse compliance requirements. The ability to isolate sensitive data within a private cloud, while leveraging the public cloud for non-critical data, allows for a tailored security approach. This flexibility enables organizations to comply with specific industry regulations and standards, such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS. This is vital for maintaining trust with customers and partners.
Comparison of Security Measures Across Cloud Environments
| Cloud Type | Security Measures |
|---|---|
| Public Cloud | Often provides a broad range of security features, including access controls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems. However, the shared responsibility model means the organization has to take ownership of many security aspects. |
| Private Cloud | Offers greater control and customization over security measures. It is often more secure from the perspective of isolation and control over the infrastructure. |
| Hybrid Cloud | Combines the security advantages of both public and private clouds. Organizations can choose the most appropriate security measures for specific data types and regulatory requirements. |
Data Sovereignty and Regulations in Hybrid Clouds
Data sovereignty and regulations are crucial considerations in hybrid cloud deployments. Hybrid clouds can address these concerns by allowing organizations to store data in regions where it is subject to specific legal requirements. This capability allows for compliance with data localization laws and regulations, such as those pertaining to data residency. By utilizing a combination of private and public cloud environments, organizations can leverage the best possible security posture for their specific data.
Security Best Practices for Hybrid Cloud Implementation
Implementing robust security measures in a hybrid cloud environment requires careful planning and execution. A key aspect is establishing clear security policies that define access controls and data encryption protocols for both public and private cloud components.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest is essential to protect against unauthorized access. This should be a core part of the security policy.
- Access Control: Implementing granular access controls for both cloud environments ensures only authorized personnel can access specific data. This is vital for maintaining compliance.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct routine security assessments and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and ensure the effectiveness of security measures. This is a continuous process.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Employing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access. This is crucial in the hybrid environment.
- Incident Response Planning: Establish a comprehensive incident response plan to address potential security breaches. This should include clear protocols and procedures for containment, eradication, and recovery.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Hybrid cloud architecture significantly enhances disaster recovery and business continuity strategies. By leveraging both on-premises and cloud resources, organizations can establish redundant systems and data backups, minimizing downtime and ensuring operational resilience in the face of unforeseen events. This approach allows for quick failover and recovery, ensuring business operations can continue uninterrupted even during significant disruptions.
Hybrid Cloud Support for Disaster Recovery
Hybrid cloud environments provide a crucial layer of redundancy for critical applications and data. By replicating data and applications in the cloud, organizations can quickly restore operations in the event of a disaster at their on-premises facility. This replication process, often automated, allows for near-instantaneous failover, significantly reducing recovery time objectives (RTOs) and minimizing financial losses.
Role of Hybrid Cloud in Maintaining Business Continuity
Hybrid cloud architectures play a vital role in maintaining business continuity by enabling organizations to rapidly transition operations to the cloud in the event of a disaster. This swift transition, coupled with the scalability of cloud resources, allows businesses to maintain service levels and operational efficiency, even during periods of high demand or system failure. The ability to scale up or down cloud resources as needed further enhances business continuity during emergencies.
Strategies for Data Backup and Recovery in a Hybrid Cloud
Implementing robust data backup and recovery strategies is paramount in a hybrid cloud environment. Organizations should leverage cloud-based storage solutions for off-site backups of critical data. This approach ensures data availability and accelerates recovery processes. Moreover, implementing automated backup and recovery mechanisms is crucial for minimizing manual intervention and ensuring quick restoration. Frequent and automated backups are essential, along with clear recovery plans, to enable a rapid restoration of services.
Case Study: Enhancing Disaster Recovery with Hybrid Cloud
A financial services company experienced a significant data breach impacting its on-premises infrastructure. Due to their hybrid cloud setup, the company quickly migrated critical applications and data to their cloud-based environment, maintaining business operations with minimal disruption. The hybrid cloud architecture enabled them to continue serving clients without any interruption, demonstrating the resilience of the solution in handling such an incident.
The rapid restoration of services, enabled by the automated backup and recovery mechanisms in the hybrid cloud, prevented significant financial losses and preserved customer trust.
Resilience of Hybrid Cloud Solutions Against Potential Failures
The resilience of a hybrid cloud solution against potential failures is a significant advantage. By replicating data and applications across different environments, hybrid cloud platforms provide multiple points of failure. This strategy mitigates the risk associated with single points of failure, increasing the overall availability and reliability of the system. Organizations can choose from various cloud providers, enhancing their resilience and providing options for disaster recovery in different geographical regions.
This redundancy and geographic diversity are key to maintaining high levels of availability and minimizing the impact of potential disruptions.
Application Deployment and Management
Hybrid cloud architectures offer unparalleled flexibility in deploying and managing applications. This adaptability allows organizations to leverage the strengths of both public and private cloud environments, optimizing resource utilization and cost-effectiveness. By strategically deploying applications across these environments, businesses can achieve greater control over sensitive data, enhance performance, and ensure robust disaster recovery capabilities.
Deployment Flexibility in a Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud model offers significant flexibility in application deployment. Organizations can choose to deploy applications in the private cloud for sensitive data or applications requiring high control. Conversely, they can utilize the public cloud for less sensitive applications or for scalability needs. This flexibility enables businesses to tailor their deployment strategy to meet specific application requirements and business needs.
This allows for a nuanced approach, ensuring that the most appropriate cloud environment hosts each application.
Application Management Strategies Across Different Environments
Effective management of applications in a hybrid cloud requires a structured approach. A key strategy is the implementation of centralized management tools. These tools facilitate consistent monitoring, patching, and updates across both public and private cloud environments. Furthermore, automation plays a crucial role in streamlining tasks like deployment, scaling, and configuration. This minimizes manual intervention and reduces the potential for errors.
Comparison to Single Cloud Model
Deploying applications in a hybrid cloud model differs significantly from a single cloud model. In a single cloud model, all applications reside in a single environment, limiting flexibility and potentially exposing sensitive data to broader risks. A hybrid approach offers a more controlled and secure environment by enabling organizations to choose the best environment for specific application needs.
It offers a layered security and scalability advantage over a single cloud model.
Application Deployment Tools and Technologies
Several tools and technologies facilitate application management in a hybrid environments. Containerization technologies like Docker allow for consistent application deployment across different cloud environments. Orchestration tools like Kubernetes automate the deployment and scaling of containerized applications. Cloud management platforms (CMPs) offer centralized management capabilities for hybrid cloud deployments, simplifying tasks like monitoring, logging, and resource allocation. This orchestration and management often improves operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Examples of Application Deployments in Hybrid Cloud Scenarios
Various examples illustrate the application of hybrid cloud deployments. A financial institution might deploy its core banking application on a secure private cloud, while using the public cloud for less critical applications like customer portals. An e-commerce company could leverage the scalability of the public cloud during peak shopping seasons while maintaining sensitive customer data in a private cloud.
These diverse examples showcase the adaptability and control offered by hybrid cloud architectures.
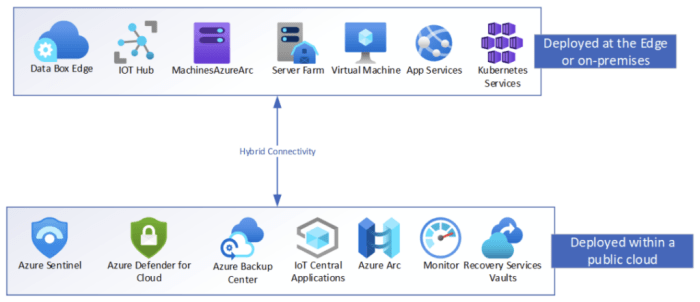
Integration with Existing Infrastructure
Hybrid cloud architectures require careful planning and execution to seamlessly integrate existing on-premises infrastructure with cloud resources. This integration process is crucial for maximizing the benefits of the hybrid model while minimizing disruption to existing operations. A well-executed integration strategy allows businesses to leverage the scalability and flexibility of the cloud while retaining the control and security of their on-premises systems.
Integrating On-Premises Infrastructure
The process of integrating existing on-premises infrastructure with a hybrid cloud involves several key steps. These steps typically include assessing the existing infrastructure, identifying critical applications and data, and planning the migration strategy. Thorough planning is paramount to avoid disruptions and ensure a smooth transition. This process necessitates careful consideration of the dependencies between on-premises systems and cloud services.
A clear understanding of the data flow and application interactions is essential to maintain business continuity during the integration process.
Challenges of Integrating Different Systems
Integrating different systems in a hybrid environment presents several challenges. One key challenge is the heterogeneity of systems and technologies. Legacy systems often use different operating systems, programming languages, and data formats compared to cloud-based services. This incompatibility can create difficulties in data exchange and application integration. Another challenge is managing data security and compliance requirements across different environments.
Maintaining consistency in security protocols and compliance standards across on-premises and cloud environments is critical. Finally, integrating different management tools and processes can also be complex.
Strategies for Seamless Integration
Several strategies can help ensure seamless integration of legacy systems into the hybrid cloud. One crucial strategy is adopting a phased approach to migration. This allows for careful testing and validation of the integration process in each phase, reducing the risk of significant disruptions. Using cloud-based services designed to interact with existing on-premises systems can facilitate the integration process.
Furthermore, adopting cloud-native technologies where appropriate can enhance the integration process and streamline future operations.
Tools and Technologies for Integration
Various tools and technologies are available to integrate on-premises systems with the cloud. These include cloud-based integration platforms that provide pre-built connectors and tools for different systems. Virtualization technologies allow for the creation of virtualized environments that can bridge the gap between on-premises and cloud-based systems. API management tools provide a standardized way to expose and manage APIs for integrating various systems.
Specialized tools are also available for migrating specific applications or databases to the cloud.
Step-by-Step Guide for Integration
A step-by-step guide for integrating existing infrastructure into a hybrid cloud involves several key steps. First, conduct a thorough assessment of the existing infrastructure to identify critical applications, data, and dependencies. Second, design a phased migration strategy, including testing and validation phases. Third, choose appropriate integration tools and technologies, considering the specific needs and characteristics of the existing infrastructure.
Fourth, implement the integration plan, ensuring data security and compliance throughout the process. Fifth, monitor the integrated environment and make necessary adjustments to ensure optimal performance and stability. Finally, maintain and optimize the hybrid environment for ongoing efficiency and scalability.
Management and Monitoring
Effective management and monitoring are crucial for a successful hybrid cloud deployment. They ensure optimal performance, security, and cost-effectiveness across on-premises and cloud environments. Proper tools and techniques are vital for seamless operation and efficient resource allocation.
Tools and Techniques for Managing a Hybrid Cloud Environment
Effective hybrid cloud management necessitates a comprehensive toolkit that spans various aspects. A key element involves using cloud management platforms (CMPs) that provide centralized control and visibility across on-premises and cloud resources. These platforms often offer automation capabilities, streamlining tasks like provisioning, configuration, and patching. Furthermore, utilizing configuration management tools is important for maintaining consistency and compliance across the different environments.
Processes for Monitoring Performance and Security in a Hybrid Cloud
Monitoring a hybrid cloud environment requires a multi-layered approach. Regular performance monitoring, including metrics such as CPU utilization, memory consumption, and network throughput, is essential for identifying potential bottlenecks and performance degradation. Security monitoring is equally critical, requiring constant vigilance for suspicious activity and adherence to established security policies. Logs from various systems must be consolidated and analyzed to detect threats and ensure compliance.
Role of Automation in Managing Hybrid Cloud Resources
Automation plays a pivotal role in streamlining hybrid cloud management. Automated tasks, like provisioning servers, deploying applications, and patching systems, reduce manual intervention and human error. This efficiency translates into cost savings and increased agility. Automation tools facilitate compliance checks and security posture assessments, improving overall operational efficiency.
Different Monitoring Tools
Numerous tools are available for monitoring a hybrid cloud environment. Examples include CloudWatch for AWS, Azure Monitor for Microsoft Azure, and Datadog for general-purpose monitoring. These platforms offer dashboards, visualizations, and alerts for a wide range of metrics, enabling proactive responses to issues. Specific tools might be needed for monitoring individual applications or components.
Management Process Flowchart in a Hybrid Cloud
 (This flowchart would visually illustrate the process, beginning with the identification of requirements, followed by the selection of appropriate cloud services and tools. Then, the process would show the implementation of these tools and services, including provisioning, configuration, and testing. Continuous monitoring and optimization are depicted next, with potential adjustments based on performance data. The final steps would involve security audits and compliance checks, culminating in a feedback loop for improvement.)
(This flowchart would visually illustrate the process, beginning with the identification of requirements, followed by the selection of appropriate cloud services and tools. Then, the process would show the implementation of these tools and services, including provisioning, configuration, and testing. Continuous monitoring and optimization are depicted next, with potential adjustments based on performance data. The final steps would involve security audits and compliance checks, culminating in a feedback loop for improvement.)
Vendor Lock-in and Choice
A key consideration in hybrid cloud deployments is vendor lock-in. Choosing a single cloud provider for all components can limit future flexibility and potentially increase costs. Understanding how different vendors interact and the potential trade-offs associated with diverse deployments is crucial. Careful planning can mitigate these risks and ensure a robust and adaptable cloud strategy.
Vendor Lock-in Considerations in Hybrid Cloud
Vendor lock-in occurs when a company becomes reliant on a particular cloud provider’s services and finds it difficult or expensive to switch to another provider. This is a significant concern in hybrid cloud setups where the organization might be using on-premises infrastructure along with services from multiple cloud providers. Choosing the right vendors for different parts of the hybrid cloud is vital to minimizing this risk.
Benefits of Using Different Vendors
Utilizing multiple cloud providers for different parts of the hybrid cloud offers several advantages. This approach allows organizations to leverage the specific strengths of each vendor. For example, one provider might excel in storage solutions, while another might be better suited for application hosting. This allows organizations to tailor their cloud environment to their specific needs and maximize performance, cost-effectiveness, and security.
Flexibility of Using Multiple Cloud Providers
Employing multiple cloud providers enhances the flexibility of the hybrid cloud architecture. This approach permits organizations to optimize their cloud environment by selecting the provider that best meets the specific requirements of each application or data set. This ensures better performance, cost savings, and improved security posture.
Advantages of Multi-Vendor Hybrid Cloud Deployments
Multi-vendor hybrid cloud deployments offer substantial advantages. By diversifying their cloud infrastructure, organizations gain greater resilience. If one provider experiences an outage or faces service disruptions, other providers can step in to maintain business operations. This also fosters competition, which can drive down costs and improve service quality.
Comparison of Hybrid Cloud Deployment Models
Different hybrid cloud deployment models have varying degrees of vendor lock-in. A model that relies heavily on a single provider for all cloud services is inherently more susceptible to vendor lock-in. Conversely, a multi-vendor model, where different parts of the infrastructure are hosted by various providers, reduces lock-in and enhances flexibility. Organizations should carefully evaluate the trade-offs associated with each model to choose the most appropriate approach for their specific needs.
Hybrid Cloud Use Cases
Hybrid cloud architecture offers a powerful approach to leveraging the strengths of both public and private clouds, tailoring the solution to specific business needs. This flexibility allows organizations to optimize resources, enhance security, and improve operational efficiency. By combining the scalability of the public cloud with the control and security of the private cloud, hybrid cloud deployments provide a robust and adaptable platform for various applications and industries.
Industries Leveraging Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud solutions are increasingly adopted across a broad spectrum of industries, each with unique requirements. The ability to seamlessly integrate on-premises systems with cloud-based services empowers businesses to address specific needs and drive innovation. The following examples demonstrate the versatility of hybrid cloud in diverse sectors.
Specific Use Cases in Various Sectors
Hybrid cloud architecture is particularly well-suited to industries requiring high levels of data security and compliance, coupled with the scalability of public cloud resources. The diverse use cases encompass various aspects of business operations, including data processing, application deployment, and disaster recovery. For instance, financial institutions utilize hybrid cloud solutions to maintain compliance with stringent regulations while benefiting from the cost-effectiveness and scalability of the cloud.
Real-World Applications in Different Sectors
Numerous organizations are successfully implementing hybrid cloud strategies to address specific challenges and achieve strategic goals. Consider a healthcare provider, where sensitive patient data is crucial. Implementing a hybrid cloud approach enables them to maintain the data on-premises, ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations, while utilizing the public cloud for data backups and non-sensitive operations. This hybrid approach allows them to maintain control over critical data while also leveraging the scalability and cost-effectiveness of the cloud.
Categorization of Industries and Their Use Cases
| Industry | Hybrid Cloud Use Case |
|---|---|
| Financial Services | Maintaining compliance with regulations, secure data storage, and high-performance transactions. Hybrid solutions enable the separation of sensitive data and applications from public cloud environments. |
| Healthcare | Meeting stringent data privacy regulations (HIPAA), while accessing cloud-based tools for data analysis, patient management, and remote access. This approach balances security with scalability and efficiency. |
| Retail | Processing large volumes of customer data, handling peak shopping seasons, and scaling inventory management systems. Hybrid solutions offer the flexibility to leverage public cloud resources for temporary spikes in demand. |
| Manufacturing | Managing complex supply chains, supporting production planning, and implementing Industry 4.0 technologies. Hybrid deployments offer secure data storage on-premises and scalable processing power in the cloud. |
| Government | Ensuring data security and compliance with stringent government regulations, while benefiting from cloud-based services for citizen engagement and e-government initiatives. |
Future Trends in Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud architectures are continuously evolving, driven by the ever-increasing demands for flexibility, scalability, and security. This evolution is fueled by the emergence of new technologies and the growing need for businesses to adapt to dynamic market conditions. The future of hybrid cloud computing promises significant advancements, enabling organizations to leverage the strengths of both public and private clouds while mitigating potential risks.
Evolving Trends in Hybrid Cloud Architecture
Hybrid cloud architectures are progressively shifting towards more automated and integrated solutions. This involves the seamless orchestration of resources across different cloud environments, reducing complexity and increasing efficiency. The focus is on developing more sophisticated tools and platforms that can simplify the management and administration of hybrid cloud deployments. Automation plays a key role in streamlining tasks, reducing manual intervention, and ensuring consistent performance.
Predictions for Future Hybrid Cloud Developments
Several predictions can be made regarding the future trajectory of hybrid cloud technologies. The adoption of serverless computing is expected to accelerate, further enabling scalability and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, the integration of edge computing into hybrid cloud architectures will become more prevalent, allowing for localized processing and analysis of data, particularly valuable for applications demanding low latency. Increased emphasis on security and compliance features is anticipated, ensuring that hybrid cloud deployments adhere to stringent industry regulations and best practices.
Role of AI and Machine Learning in Hybrid Cloud
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to significantly impact hybrid cloud architectures. AI-powered tools will automate tasks such as resource allocation, security threat detection, and performance optimization. ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from different cloud environments to predict future needs and proactively adjust resources, optimizing costs and performance. These advancements will contribute to a more intelligent and self-managing hybrid cloud infrastructure.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Hybrid Cloud Strategies
Emerging technologies, such as quantum computing and blockchain, are also likely to influence hybrid cloud strategies. Quantum computing, though still in its nascent stages, may eventually impact certain computationally intensive tasks, potentially finding a niche within specific hybrid cloud applications. Blockchain technology could revolutionize data security and management within hybrid cloud environments, offering enhanced transparency and trust in data sharing and transactions.
This integration will necessitate adaptation and careful consideration of security implications and practical implementation challenges.
Forecast for the Future of Hybrid Cloud Computing
The future of hybrid cloud computing is bright, with numerous opportunities for innovation and growth. Organizations will continue to leverage hybrid cloud solutions for improved scalability, cost-effectiveness, and agility. The integration of emerging technologies will drive the evolution of hybrid cloud, potentially leading to a future where cloud environments are more automated, intelligent, and secure. This, in turn, will empower businesses to adapt to dynamic market conditions and optimize their operations across different cloud environments.
Summary
In conclusion, hybrid cloud architecture provides a flexible and robust solution for organizations seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure. Its adaptability, scalability, and security features offer a powerful advantage, supporting business continuity and disaster recovery strategies. The benefits of a hybrid cloud strategy are numerous and extend to various industries, demonstrating its enduring relevance in the ever-evolving IT landscape.
Top FAQs
What are the key components of a hybrid cloud setup?
Key components include a private cloud infrastructure, a public cloud platform, and the integration mechanisms to connect them. This often involves specialized software and tools to ensure seamless communication and data flow between the two environments.
How does hybrid cloud improve data security?
Hybrid cloud environments allow businesses to store sensitive data in their private cloud while leveraging the security features and compliance standards offered by public cloud providers. This approach often results in more robust security postures compared to either model alone.
What are some common challenges in implementing hybrid cloud?
Challenges can include ensuring data consistency and security across different environments, managing the complexities of integration, and maintaining compliance across both public and private cloud components. Proper planning and management are crucial for a successful implementation.
How can a business choose the right hybrid cloud vendors?
Businesses should consider factors like the specific needs of their applications, data storage requirements, and security compliance mandates when selecting vendors. A thorough evaluation of the capabilities and reliability of potential vendors is essential.